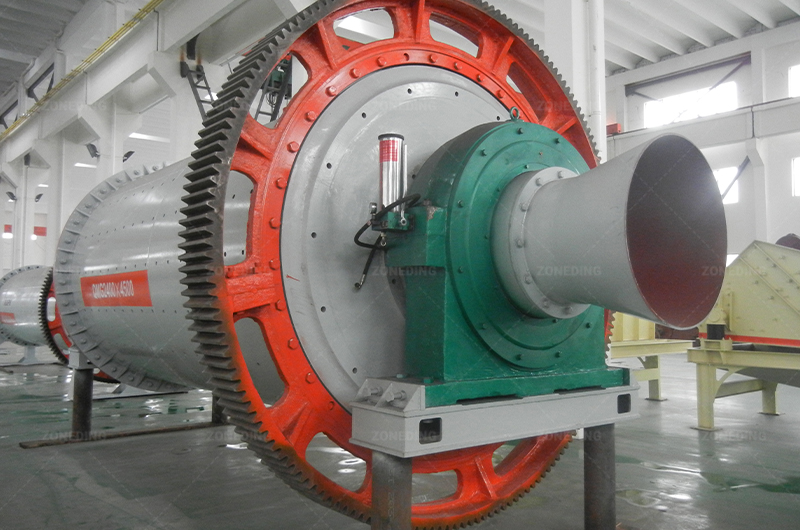
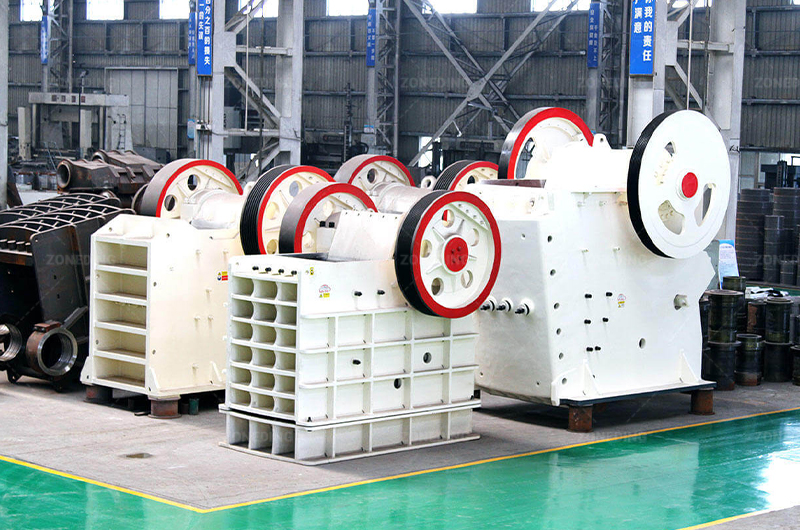
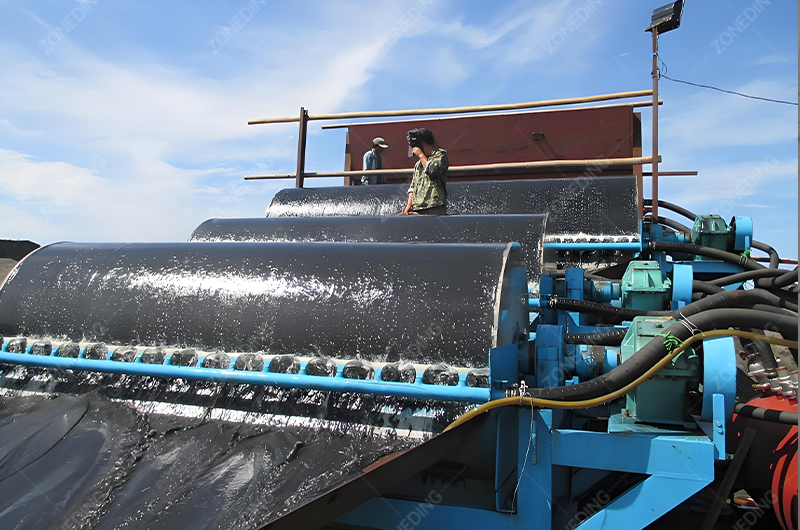
Tantalum Niobium Ore Processing Plant Solutions
Tantalum niobium ore is a broad term that encompasses minerals containing tantalum and niobium, primarily extracted from tantalite (coltan), niobium iron ore (columbite), and pyrochlore.
To tailor tantalum niobium ore processing plants and mining equipment and suit the specific requirements of different ore types, These customized solutions include a wide range of processes such as washing, crushing, grinding, gravity separation, magnetic separation, drying, and more.
How to Unlock Tantalum and Niobium Extraction: Overcoming Technical Hurdles from Mining to Refining?
Successful tantalum and niobium extraction requires a multi-stage approach. This starts with physical concentration methods. It then moves to complex chemical processing, often using hydrofluoric acid and solvent extraction. Managing radioactivity and ensuring safety are critical throughout.
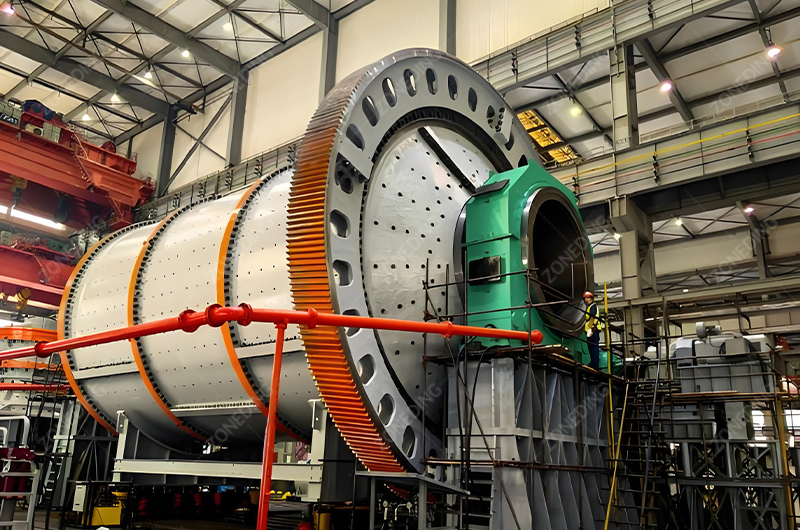
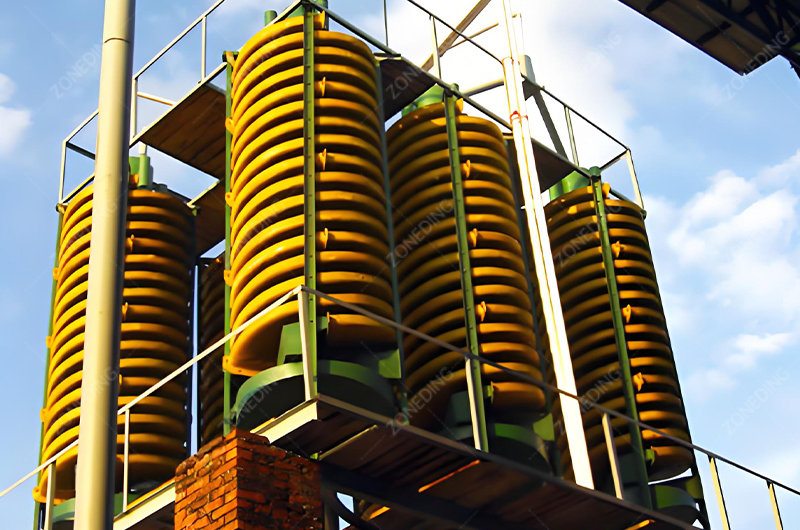



Extracting these valuable metals is not straightforward. It demands careful planning, specialized knowledge, and robust equipment.
Why is Efficient, Safe Tantalum-Niobium Ore Processing Crucial for High-Tech Industries?
Efficient and safe processing is vital because tantalum and niobium are irreplaceable in many high-tech applications. Supply disruptions or unsafe practices directly impact industries relying on components like capacitors, superalloys, and advanced electronics.


Fueling Modern Technology
Tantalum and niobium are not just commodities; they are enabling elements for technological progress. Their unique properties make them essential.
- Critical Applications:
- Tantalum: Primarily used in high-performance capacitors for electronics (smartphones, laptops, automotive systems) due to its high capacitance in small volumes. Also used in corrosion-resistant equipment and surgical implants.
- Niobium: Widely used as an alloying agent in high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels for pipelines and structures. Crucial in superalloys for jet engines and rockets due to its high-temperature strength. Also used in superconducting magnets (MRI machines, particle accelerators).
- Supply Chain Security:The high-tech sectors depend on a stable and predictable supply of these metals. Inefficient processing leads to waste and higher costs. Unsafe practices can halt production due to accidents or regulatory shutdowns. Both scenarios create supply chain vulnerability.
- Economic Impact:Reliable processing underpins the manufacturing of countless devices and infrastructure projects. Ensuring a steady flow of Ta and Nb supports global economic activity in key technological sectors.
Therefore, mastering the complexities of Ta-Nb processing isn’t just about optimizing one mine site. It’s about ensuring the foundation for critical global industries remains strong and secure. ZONEDING contributes by providing reliable initial Crushing and grinding equipment (Ball Mill) for the start of this vital chain.
Is The Ore Primarily Tantalite, Columbite, or Pyrochlore? How Does Mineral Type Affect Processing Choices?
The specific mineralogy drastically affects processing choices. Tantalite/columbite ores are often amenable to physical separation (gravity, magnetic). Pyrochlore/microlite ores are typically more complex and often require direct chemical leaching for efficient recovery.



Mineralogy Dictates the Flowsheet
Understanding the primary host mineral for tantalum and niobium is the first critical step in designing an effective processing plant. Different minerals have different physical and chemical properties.
| Mineral Group | Typical Formula Example | Key Characteristics | Primary Processing Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tantalite-Columbite | (Fe,Mn)(Ta,Nb)₂O₆ | Relatively dense, often well-crystallized, weak magnetic | Physical Separation: Gravity concentration (Jigs, Tables, Spirals), Magnetic Separation (Magnetic Separator), sometimes flotation. Pre-concentration is key. |
| Pyrochlore-Microlite | (Na,Ca)₂(Nb,Ta)₂O₆(O,OH,F) | Often finer-grained, complex structures, variable density | Chemical Leaching: Often requires direct acid attack (like HF) for breakdown. Physical methods may be less effective or only for pre-concentration. Flotation sometimes used. |
| Other Ta/Nb Minerals | Wodginite, Ixiolite, Simpsonite etc. | Variable properties, often associated with Li-pegmatites | Processing depends heavily on specific mineral properties and associations. Requires detailed mineralogical study. |
- Tantalite-Columbite Series: These are the most common sources. Their relatively high density allows effective concentration using gravity methods after crushing and grinding. Their weak magnetic properties allow separation from non-magnetic gangue using high-intensity magnetic separators.
- Pyrochlore Group: These minerals often occur in carbonatites or alkaline rocks. Their structure makes them more resistant to physical breakdown and separation. Direct chemical leaching is often the preferred route, sometimes after some initial physical upgrading if possible.
- Importance of Analysis: Before investing in equipment or designing a flowsheet, detailed mineralogical analysis (using techniques like XRD, SEM-EDS) is essential. This identifies the exact minerals, their grain size, how they are intergrown (liberation characteristics), and associated gangue minerals. This knowledge prevents costly mistakes in process selection.
Knowing your ore type is fundamental. It dictates whether you lean towards physical methods (where ZONEDING equipment excels) or need to prepare for more complex chemical routes early on.
How Can Effectively Pre-Concentrate Low-Grade Tantalum-Niobium Minerals Using Physical Methods like Gravity and Magnetic Separation?
Gravity and magnetic separation are crucial and cost-effective methods to pre-concentrate low-grade tantalite/columbite ores. Effective use requires careful sizing (classification) and often multiple stages of separation using different equipment types.
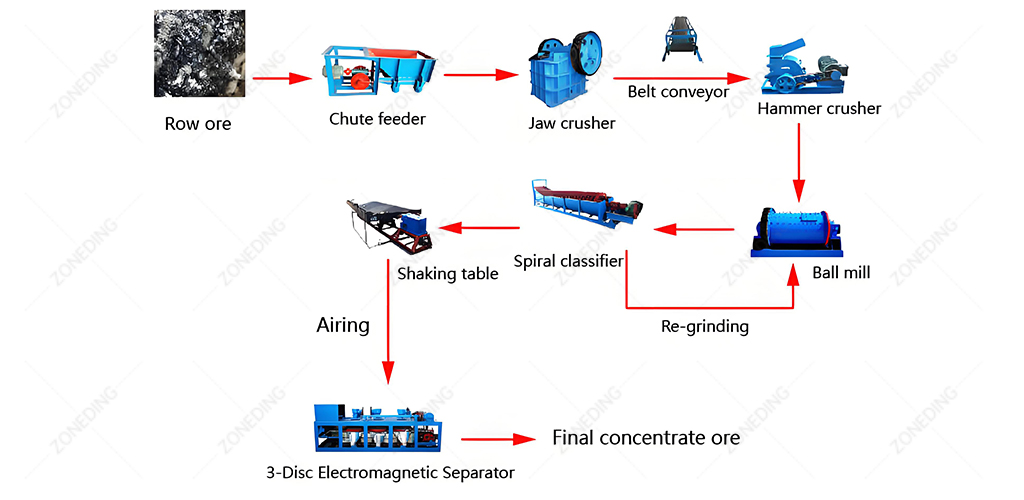
Building the Foundation with Physical Separation
For ores where Ta-Nb minerals are sufficiently liberated and denser/more magnetic than the gangue (waste rock), physical separation is the economic backbone of processing.
- Importance of Sizing : Ta-Nb minerals often have variable grain sizes. Different separation devices work best on different size ranges. Crucially, the ore must be carefully sized using screens (Vibrating Screens) before separation. Feeding a wide size range to a single device drastically reduces efficiency. This is a common failure point.
- Gravity Separation Methods: Exploits the high density of Ta-Nb minerals.
- Coarse Particles: Jigging Separator Machines often used for particles >1mm.
- Medium Particles: Shaking Tables are effective for sand-sized particles (e.g., 0.1-1mm).
- Fine Particles: Spiral Chutes can treat finer sands. For very fine particles (<74 microns), enhanced gravity devices like centrifugal concentrators (e.g., Falcon, Knelson) are often necessary as traditional methods lose efficiency. A multi-stage approach using different devices for different size fractions is key.
- Magnetic Separation: Tantalite-columbite minerals are weakly magnetic (paramagnetic).
- Low Intensity Magnetic Separation (LIMS): Removes strongly magnetic minerals like magnetite first (using equipment like drum Magnetic Separators).
- High Intensity Magnetic Separation (HIMS): Used to separate the weakly magnetic Ta-Nb minerals from non-magnetic gangue (quartz, feldspar). Both dry and wet HIMS systems exist. Effective magnetic separation requires dry, clean feed material within a narrow size range. Proper drying and screening are essential pre-treatment steps.
- Electrostatic Separation: Can sometimes be used after magnetic separation to separate conductive minerals (like Ta-Nb oxides, ilmenite) from non-conductive ones (like zircon, quartz). This also requires very dry feed, precise sizing, and controlled atmospheric conditions (humidity).
- Associated Minerals: These physical separation steps often also concentrate other valuable heavy minerals present in the ore, such as cassiterite (tin), zircon, monazite (REE), ilmenite (titanium). Recovering these byproducts can significantly improve project economics.
ZONEDING provides a wide range of reliable Crushing Equipment, grinding mills (Ball Mills), Vibrating Screens, and separation equipment (Jigs, Tables, Spirals, Magnetic Separators) needed for these critical pre-concentration stages. Properly designed multi-stage physical separation is fundamental to economically processing most Ta-Nb ores.
Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) Digestion: How to Safely and Efficiently “Unlock” Stubborn Tantalum-Niobium Minerals?
HF acid digestion effectively breaks down refractory Ta-Nb minerals by forming soluble fluoride complexes. However, HF is extremely hazardous. Its use demands specialized corrosion-resistant equipment, rigorous safety protocols, extensive worker training, and emergency preparedness.

The Power and Peril of HF
Hydrofluoric acid is often necessary for chemically processing Ta-Nb concentrates, especially those resistant to other reagents.
- Why HF Works: Tantalum and niobium oxides react with HF to form stable, soluble fluoride complexes (e.g., H₂TaF₇ and H₂NbOF₅). This effectively dissolves the minerals, allowing Ta and Nb to enter an aqueous solution for further separation and purification. Often, sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) is used alongside HF to help decompose associated minerals and manage reaction products.
- When is it Used : HF digestion is a high-cost, high-risk process. It’s typically applied to pre-concentrates obtained from physical separation, not directly to low-grade run-of-mine ore. It might also be considered for very complex or refractory ores where physical methods fail.
- Extreme Danger: HF is one of the most dangerous industrial chemicals. It causes severe, deep burns that may not be immediately painful but can be fatal even from skin contact over a small area. It penetrates tissue and depletes calcium, potentially causing systemic toxicity and cardiac arrest. Inhalation is also extremely dangerous.
- Safety is Paramount:
- Equipment: Requires specialized equipment made from HF-resistant materials (e.g., plastics like PTFE, PFA, PVDF; certain specialized alloys – NOT glass or standard stainless steel). Excellent ventilation (fume hoods) is mandatory.
- Protocols: Strict operating procedures, rigorous training, mandatory Personal Protective Equipment (PPE – specialized gloves, aprons, face shields), leak detection systems, and restricted access zones are essential.
- Emergency Response: Readily available calcium gluconate antidote (gel for skin, potentially solutions for washing/injection under medical supervision), emergency showers/eyewash stations, and well-rehearsed emergency plans are non-negotiable.
Using HF is a serious undertaking. The potential benefits of unlocking stubborn minerals must be weighed against the significant risks and the high costs associated with safe handling, specialized equipment, and waste treatment.
Tantalum-Niobium Separation is the Core Difficulty: How Does Solvent Extraction (SX) Technology Achieve This Challenge?
Solvent Extraction (SX) is the dominant technology for separating Ta and Nb. It uses specific organic liquids (solvents) that selectively pull either tantalum or niobium fluoride complexes out of the acidic aqueous solution, leaving the other behind. This allows for highly efficient separation.
The Chemical Sorting Machine: SX
Separating tantalum and niobium is challenging due to their near-identical chemical behavior. Solvent extraction provides an elegant solution by exploiting subtle differences in how their fluoride complexes distribute between two immiscible liquids.
- The Chemical Similarity Problem: Ta and Nb sit next to each other in the periodic table and share many chemical properties, making traditional precipitation methods difficult for achieving high purity separation.
- How SX Works:
- Extraction: The acidic aqueous feed solution (containing dissolved TaF₇²⁻ and NbOF₅²⁻ complexes from HF digestion) is mixed vigorously with an immiscible organic solvent. Common solvents include methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK) or tributyl phosphate (TBP) diluted in kerosene. Under specific acidity (HF/H₂SO₄ concentration) conditions, the organic solvent selectively bonds with and extracts one element’s complex (often Ta) more strongly than the other.
- Separation: The mixture is allowed to settle. The lighter organic phase (now loaded with Ta) separates from the heavier aqueous phase (raffinate, containing most of the Nb and impurities).
- Scrubbing (Optional): The loaded organic phase might be washed with a specific aqueous solution to remove any co-extracted impurities.
- Stripping: The loaded organic phase is then contacted with another aqueous solution (e.g., dilute acid or water) under conditions that reverse the extraction, transferring the purified Ta back into a new aqueous solution (strip solution).
- Niobium Recovery: The niobium remaining in the initial aqueous raffinate can then be extracted using different conditions or solvents, or recovered by other means.
- Key Factors: The efficiency and selectivity of SX depend heavily on precise control of acid concentrations (HF, H₂SO₄), phase ratios (organic:aqueous), contact time, and temperature. The process is typically carried out in multi-stage mixer-settler units to achieve high purity.
Solvent extraction is a powerful but complex chemical engineering process. It requires sophisticated plant design, careful operation, and management of potentially flammable and volatile organic solvents, in addition to the corrosive aqueous feed.
Besides Solvent Extraction, What Other Technical Routes Are Available for Tantalum-Niobium Separation?
While SX is dominant, older methods like fractional crystallization (Marignac process) exist but are less efficient. Ion Exchange (IX) chromatography offers another potential route, capable of high selectivity but often with lower throughput and potentially higher resin costs.
Exploring Other Separation Pathways
While SX holds the top spot for industrial-scale, high-purity separation, other techniques have been used or explored.
- Fractional Crystallization (Marignac Process):
- Principle: This historical method relies on the difference in solubility between potassium heptafluorotantalate (K₂TaF₇) and potassium oxypentafluoroniobate (K₂NbOF₅) in dilute HF solutions. K₂TaF₇ is less soluble and crystallizes out first upon cooling or evaporation, leaving K₂NbOF₅ in solution.
- Pros: Relatively simpler concept than SX.
- Cons: Requires multiple, carefully controlled crystallization steps to achieve high purity. Separation is often incomplete, leading to lower yields or cross-contamination. Generates large volumes of fluoride-containing solutions. Largely superseded by SX for high-purity production.
- Ion Exchange (IX) Chromatography:
- Principle: Uses specialized solid resins that have charged functional groups. The Ta and Nb fluoride complexes (which are anions like TaF₇²⁻ and NbOF₅²⁻) can bind to anion exchange resins. By carefully controlling the composition of the solution passed through the resin column (e.g., changing HF/HCl concentrations), Ta and Nb can be selectively adsorbed and then eluted (washed off) separately.
- Pros: Can achieve very high purity separation. Potentially avoids large volumes of organic solvents used in SX.
- Cons: Can be a slower process (lower throughput) compared to SX. Resins can be expensive and may degrade over time, especially in strong acid conditions. May still require HF in the feed solutions. More common in analytical or smaller-scale applications, though potentially viable for specific industrial scenarios.
While these alternatives exist, solvent extraction remains the workhorse for large-scale industrial separation of tantalum and niobium due to its efficiency and ability to handle continuous flows effectively, despite its complexity and reliance on HF.
How To Deal with Worrying Associated Radioactive Elements (Uranium, Thorium) During Processing?
Radioactive elements (U, Th) are a major concern. They require strict radiation monitoring, worker protection, specialized waste management, and often specific chemical steps (like precipitation or selective extraction) during processing to remove them from the main Ta-Nb streams.
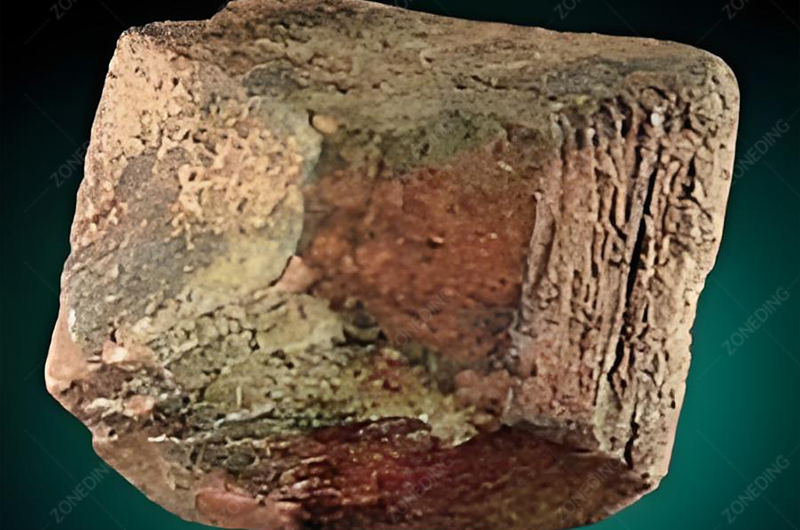
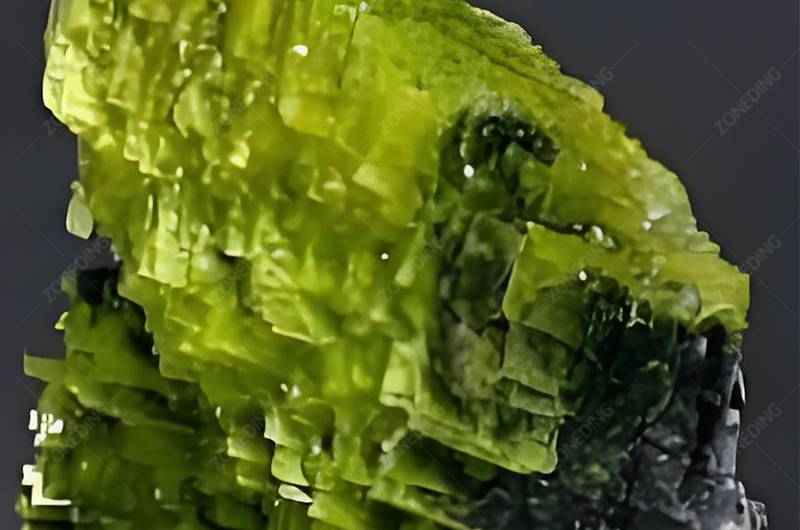



The Radioactivity Challenge
The common co-presence of uranium and thorium with tantalum and niobium ores presents significant technical, safety, and economic challenges. It’s far more than just a health issue.
- The Source: U and Th often substitute into the crystal lattice of Ta-Nb minerals or occur as discrete associated minerals (like uraninite, thorite).
- Safety Measures: Requires implementation of radiation protection programs based on the ALARA principle (As Low As Reasonably Achievable). This includes:
- Monitoring radiation levels in work areas and on materials.
- Controlling dust generation (as inhaled radioactive dust is particularly hazardous).
- Using appropriate PPE.
- Implementing shielding where necessary.
- Regular health checks for workers.
- Waste Management: Tailings, leach residues, and equipment contaminated with Naturally Occurring Radioactive Material (NORM) or Technologically Enhanced NORM (TENORM) require special handling and disposal. This involves:
- Designated storage areas.
- Engineered containment (e.g., lined tailings dams) to prevent environmental contamination.
- Compliance with strict national and international regulations regarding radioactive waste. This can be extremely expensive .
- Chemical Removal: During chemical processing (like SX or precipitation), conditions can often be adjusted to separate U and Th from Ta and Nb. For example, U and Th might precipitate under different pH conditions or be selectively extracted by different solvents or stages in an SX circuit. Removing them is crucial for final product quality.
- Economic and Market Impact: This is critical.
- High Costs: Environmental assessments, licensing, specialized waste disposal, and safety measures add significant cost.
- Transport Restrictions: International regulations (IATA for air, IMO for sea) strictly limit the transport of radioactive materials, adding complexity and cost, or even prohibiting shipment if limits are exceeded.
- Market Access: Many buyers and refiners have strict limits on U+Th content in Ta-Nb concentrates. Exceeding these limits leads to significant price penalties or outright rejection of the material. Underestimating the economic impact of radioactivity is a major pitfall.
Addressing radioactivity must be a primary consideration from the very beginning of project evaluation. Accurate measurement of U and Th, understanding their mineralogical form, and planning for their management throughout the flowsheet and waste streams are essential for technical feasibility, regulatory compliance, and economic viability.
What Steps Are Needed to Get from Pure Tantalum/Niobium Solutions to Final High-Purity Oxides or Metals?
Pure Ta and Nb solutions are typically treated to precipitate the metals as hydroxides or salts. These precipitates are then washed, dried, and calcined (heated) to produce high-purity oxides (Ta₂O₅, Nb₂O₅). Producing pure metal requires further complex reduction steps.
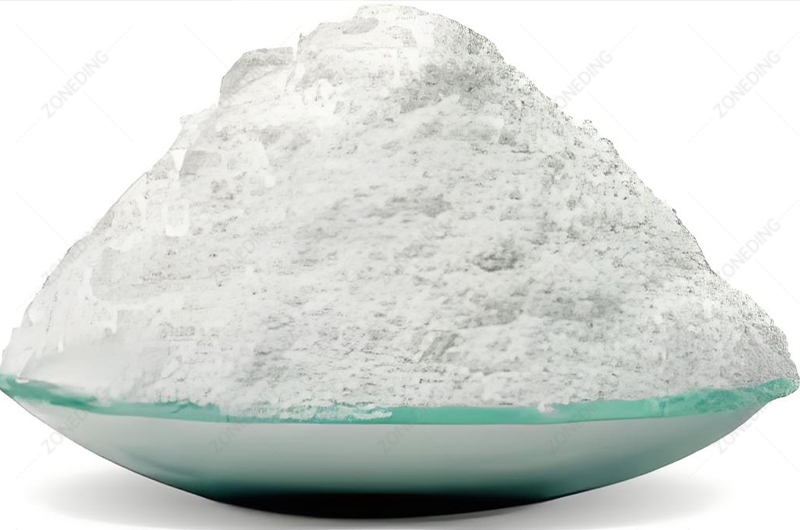
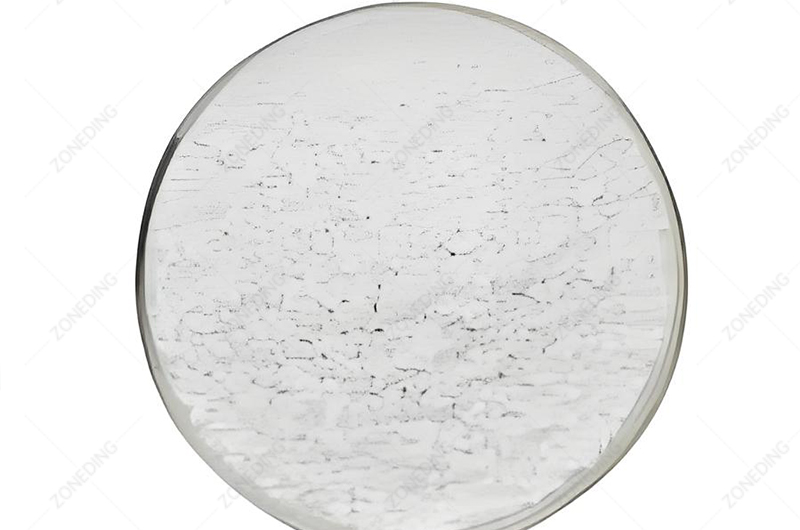


From Solution to Solid Product
The final steps involve converting the purified aqueous solutions from SX or other separation methods into stable, marketable forms.
- Precipitation:
- Hydroxides: Adding ammonia (NH₃) or ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH) to the purified Ta or Nb strip solutions causes tantalum hydroxide (Ta(OH)₅) or niobium hydroxide (Nb(OH)₅) to precipitate as white solids. Careful pH control is needed for complete precipitation and purity.
- Fluoride Salts: Alternatively, for tantalum, adding potassium fluoride (KF) or potassium chloride (KCl) can precipitate potassium heptafluorotantalate (K₂TaF₇), a key intermediate for metal production.
- Washing: The precipitated solids must be thoroughly washed to remove residual processing chemicals.
- Calcination to Oxides:
- The washed hydroxide precipitates are dried and then calcined (heated to high temperatures, e.g., 800-1000°C) in a furnace. This drives off water and converts the hydroxides into stable, high-purity tantalum pentoxide (Ta₂O₅) or niobium pentoxide (Nb₂O₅). These white powders are common final products sold for various applications (e.g., making capacitors, optical glass, alloys).
- Metal Production: Producing pure tantalum or niobium metal requires further high-temperature reduction processes:
- Tantalum Metal: Commonly produced by sodium reduction of K₂TaF₇ (reduction with molten sodium metal under inert atmosphere) or by electrolysis of molten K₂TaF₇ salt mixtures. The resulting metal powder is then consolidated by pressing and vacuum sintering.
- Niobium Metal: Often produced by aluminothermic reduction of Nb₂O₅ (reduction with aluminum powder) or by electrolysis. Electron beam melting is frequently used for final purification and consolidation of both metals.
These final refining steps require specialized high-temperature equipment and careful control to achieve the desired purity levels required by different industries. The choice between producing oxides or metal depends on the target market and the processor’s capabilities.
What Special Requirements Do Tantalum-Niobium Processing Plants Have for Equipment? (Corrosion Resistance, Radiation Shielding, etc.)
Ta-Nb processing demands equipment with exceptional corrosion resistance, especially for stages using HF. Materials like specialized plastics (PTFE, PVDF) and certain alloys are necessary. Depending on radioactivity levels, radiation shielding might also be required in specific areas.



Built to Withstand the Extremes
Standard construction materials are often inadequate for the aggressive chemical environments and potential radiological hazards encountered in Ta-Nb processing.
- Corrosion Challenge (HF Handling): Hydrofluoric acid is extremely corrosive to many common materials, including glass, ceramics, and most metals (including stainless steel).
- Material Choices: Equipment handling HF solutions (tanks, pipes, pumps, valves, reactors) must be made from resistant materials. Commonly used options include:
- Fluoropolymers: PTFE (Teflon™), PFA, PVDF, ECTFE. These offer excellent resistance but have temperature and pressure limitations.
- Other Plastics: Polypropylene (PP) and Polyethylene (PE) may be suitable for lower concentrations or temperatures.
- Specialized Alloys: Certain high-nickel alloys (like Monel® or Hastelloy®) may offer resistance under specific conditions but are expensive. Carbon brick lining is sometimes used in reactors.
- Material Choices: Equipment handling HF solutions (tanks, pipes, pumps, valves, reactors) must be made from resistant materials. Commonly used options include:
- Solvent Extraction (SX) Equipment: Needs resistance to both the acidic aqueous phase and the organic solvent phase. Materials like polypropylene, PVDF, or sometimes specialized stainless steels or alloys are used for mixer-settlers, tanks, and piping. Robust seals resistant to organic solvents are critical.
- Radiation Shielding Considerations: If processing materials with significant U/Th content, shielding might be necessary around certain equipment or areas (like concentrate storage, leach reactors, waste handling) to protect workers. The type and thickness of shielding (e.g., lead, concrete) depend on the measured radiation levels.
- General Robustness: Even in the initial physical separation stages, equipment must be robust and reliable for mining duty. ZONEDING’s Crushing Equipment, Ball Mills, Magnetic Separators, and gravity separation units are designed for durability in these demanding environments.
Selecting appropriate materials of construction is critical for plant longevity, operational safety, and preventing product contamination. The highly specialized nature of chemical processing equipment often requires sourcing from manufacturers with specific expertise in handling corrosive and hazardous materials.
Facing HF Hazards and Radioactivity: What Are the Best Practices for Safety and Environmental Protection?
Best practices involve rigorous HF safety protocols (training, PPE, emergency response), strict radiation controls (monitoring, ALARA), robust ventilation and leak detection, secure waste containment and disposal according to regulations, and a strong overall safety culture.


Operating Responsibly with Hazardous Materials
Safety and environmental protection are non-negotiable aspects of Ta-Nb processing due to the inherent hazards.
- HF Safety Protocols:
- Training: Comprehensive and regular training for all personnel handling or working near HF.
- PPE: Mandatory use of appropriate, HF-resistant PPE (gloves, face shields, aprons/suits).
- Handling: Use in designated areas with excellent ventilation (fume hoods). Strict procedures for transfer and use.
- Emergency Response: Immediate access to calcium gluconate antidote, emergency showers/eyewash, spill kits, and trained first responders. Clear emergency procedures.
- Radiation Protection (ALARA):
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring of radiation levels in materials and work areas. Personal dosimeters for workers.
- Time, Distance, Shielding: Minimize exposure time, maximize distance from sources, use shielding where necessary.
- Containment: Control dust; use sealed systems where possible.
- Waste Management:
- Acid Neutralization: Systems to safely neutralize waste acid streams before discharge or disposal.
- Heavy Metal Removal: Precipitation or other methods to remove dissolved metals from effluents.
- Radioactive Waste: Secure, long-term storage or disposal of radioactive residues and tailings in engineered facilities compliant with all national and international regulations. This is often the most complex and costly environmental challenge.
- Ventilation and Leak Detection: Robust ventilation systems in all chemical processing areas. Continuous monitoring systems for HF leaks or other hazardous vapors.
- Safety Culture: Fostering a workplace culture where safety is the top priority, procedures are strictly followed, and reporting of concerns is encouraged.
Implementing and consistently enforcing these best practices is essential to protect workers, the environment, and the surrounding community, and to ensure the long-term sustainability and social license to operate for any Ta-Nb processing facility.
When Looking for Tantalum-Niobium Processing Technology or Equipment Partners, What Key Capabilities Should We Look For?
Prioritize partners with proven, specific experience in tantalum-niobium processing. Look for deep understanding of both mineralogy/beneficiation and chemical processing complexities (including HF safety and radioactivity management). Assess their testing capabilities, commitment to safety/environment, and knowledge of final product market specifications.



Advantages of ZONEDING MACHINE
Selecting knowledgeable and experienced partners is critical for navigating the challenges of Ta-Nb extraction.
- Proven Ta-Nb Expertise: Look beyond general mining or chemical processing experience. As your reliable partners (consultants, engineering firms, equipment suppliers, labs) with a demonstrated track record specifically in designing, equipping, or operating successful Ta-Nb plants, ZONEDING can provide references and relevant case studies.
- Understanding of Complexities: ZONEDING can grasp the unique challenges:
- Mineralogical nuances and their impact on flowsheet design.
- Intricacies of physical separation.
- Safe handling of HF and design of resistant systems.
- Management of radioactivity (technical, safety, regulatory, economic aspects).
- Chemistry of leaching and separation (SX, alternatives).
- Testing Capabilities: ZONEDING involved in process design have access to well-equipped laboratories and potentially pilot plant facilities to conduct thorough metallurgical test work on your specific ore. This is crucial for optimizing the flowsheet.
- Safety & Environmental Commitment: ZONEDING ensure safety and environmental responsibility. ZONEDING’s designs and practices reflect best-in-class standards for handling hazardous materials and waste.
- Understanding Market Needs: Crucially, ZONEDING understand the final product specifications required by smelters and buyers. ZONEDING can help design a process that produces a marketable concentrate meeting specific Ta/Nb ratio, purity, particle size, and impurity (especially U, Th, Sn, Ti) requirements. Producing an off-spec product is useless, regardless of recovery.
- Equipment Reliability and Suitability: For equipment suppliers like ZONEDING, reliability and suitability for the specific stage are key. ZONEDING provides robust and customizable equipment for the demanding initial beneficiation stages (Crushing Equipment, Ball Mills, screens, gravity and magnetic separators), forming a reliable foundation for the downstream processes.
Choosing partners wisely, based on demonstrated specific expertise and a holistic understanding of the technical, safety, environmental, and market challenges, is fundamental to success in the complex world of tantalum and niobium processing.
Conclusion
Extracting tantalum and niobium is a complex journey. It blends advanced physical separation with challenging chemical processes, demanding rigorous safety and environmental controls. Success requires deep expertise, careful planning, robust equipment, and knowledgeable partners like ZONEDING for key stages.
 Zoneding Machine
Zoneding Machine


